Gathering User Input
In Making and Receiving Phone Calls we learned the basics of using cXML Scripts to define the behavior of phone calls. In this article, we are going to see how to gather input from the user.
In general, there are three kinds of input that you could want to gather: keypad input, text input via speech recognition, and audio recordings. In this article we are going to focus on keypad input and speech recognition.
cXML for Gathering Input
We are going to define the forwarding instructions in an cXML Script hosted on SignalWire.
- New Dashboard
- Legacy Dashboard
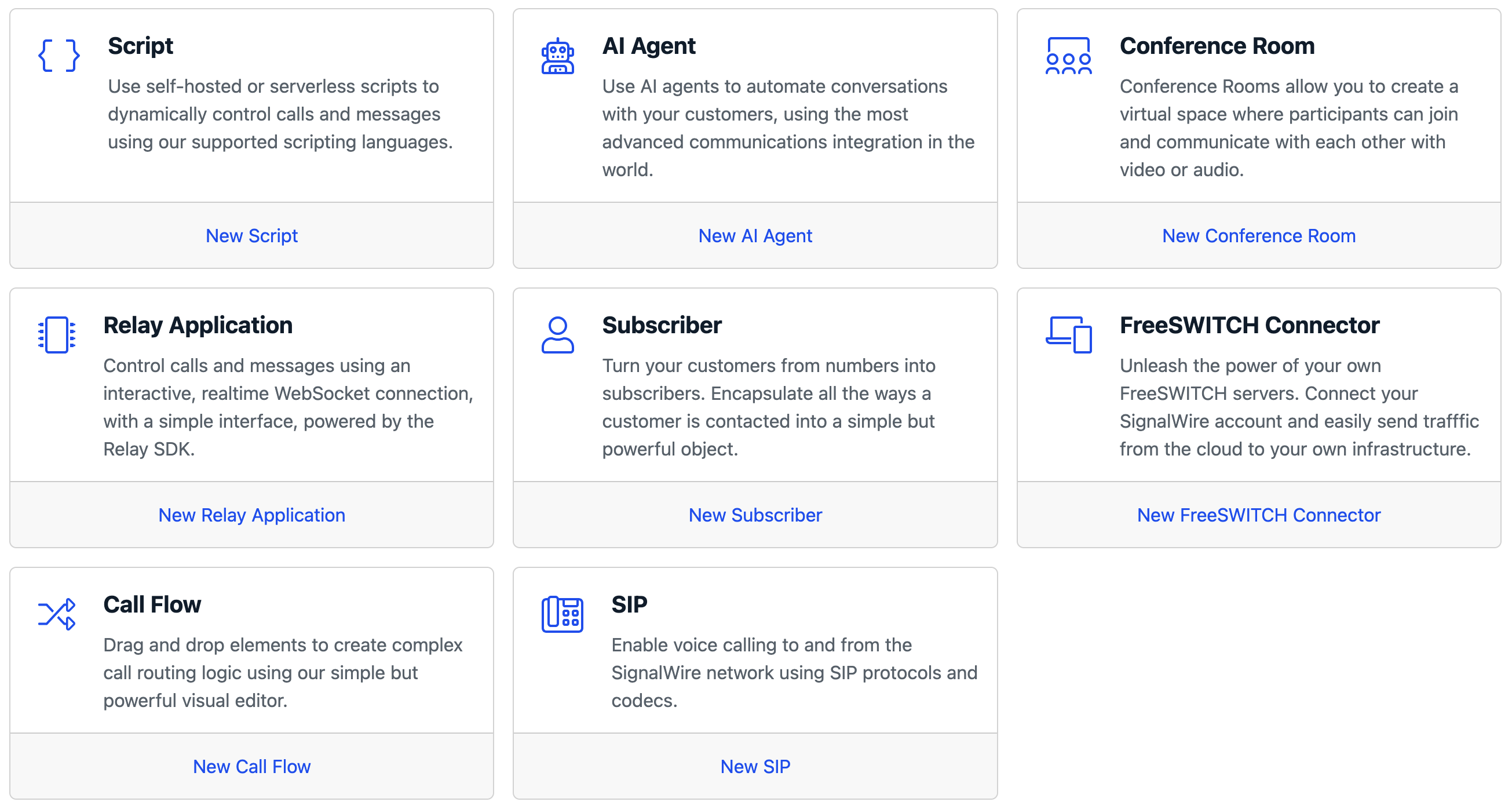
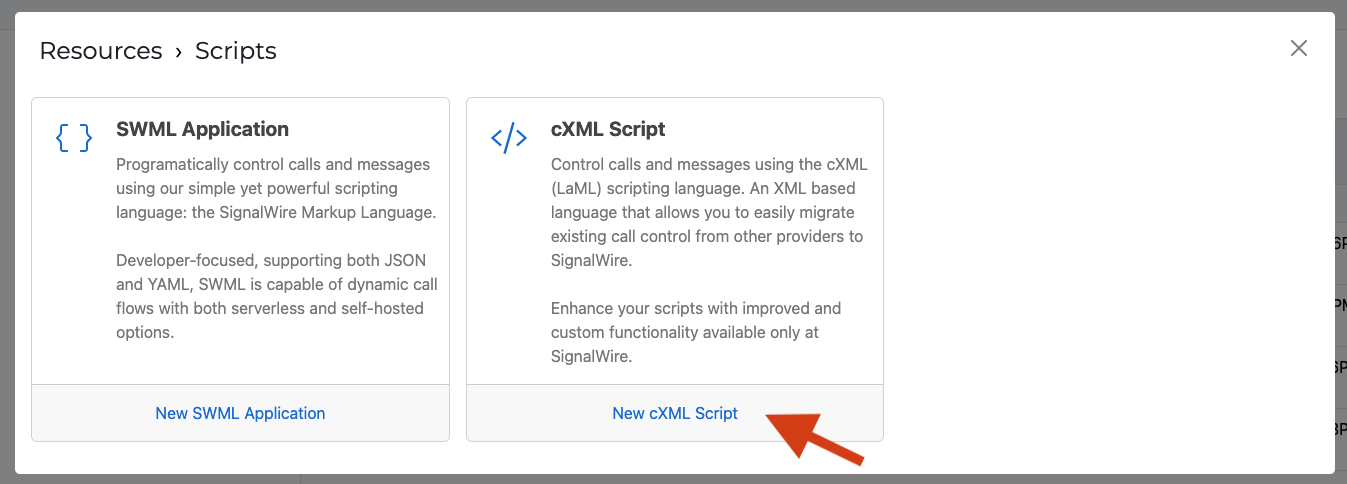
If you're on the new UI, go to the Resources section from the sidebar, and create a new Resource. In the new resource picker, select Script and create a cXML script.
If you're on the Legacy UI, go to the cXML/LaML section in your SignalWire Space, then click on Bins, and create a new script.
Paste the following XML content in your new cXML Script:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Response>
<Gather
input="speech dtmf"
action="https://example.com/my-webhook"
timeout="5"
numDigits="5"
hints="one two three four five six seven eight nine">
<Say>
Welcome! Please enter or say your account number.
</Say>
</Gather>
<Say>No input detected.</Say>
<Hangup />
</Response>
We used the <Gather> verb to gather input as soon as the call starts. We set five attributes:
input, which specifies which kind of input we want to gather (in our case, both speech and DTMF keypad input);action, which specifies the URL to fetch when the input has been collected (the URL should return a new cXML document to execute);timeout, i.e., the number of seconds of silence or inaction that denote the end of caller input;numDigits, which indicates the number of digits to collect via DTMF keypad input; andhints, an optional list of words to help the speech recognition algorithm.
Within the <Gather> verb, we nested <Say> in order to play some instructions.
When input gathering completes, the script will fetch the URL specified in
action and will execute it. If, instead, no input is detected within the
timeout, then the following instructions keep executing: in our case, we say "no input detected" and hang up.
If you're still on Legacy UI, refer to Making and Receiving Phone Calls for detailed instructions.
Reading the User Input
When fetching the Gather's action URL, SignalWire includes some parameters such as:
From: the caller's numberTo: the callee's numberDigits: DTMF digits gathered from the user, if anySpeechResult: Speech input gathered from the user, if any- ...more
With a custom web server, you can read these parameters and, depending on their value, emit a different cXML document to execute. You can easily test this with sites such as https://webhook.site, which allow you to view the details for incoming webhook requests. For more information on how to use your web server for gathering user input, see Gathering User Input from Code.
Assigning the Bin to a SignalWire Phone Number
The final step is to configure one of your SignalWire phone numbers to answer calls using the cXML Script we just created. You can do that from the "Phone Numbers" section:
Refer to Making and Receiving Phone Calls for more information about this step.
Conclusion
cXML Scripts offer a quick and easy way to get started with common use cases. If you are an advanced developer, or you need more flexibility and real-time control on your calls, you may be interested in our guide about how to make and receive calls in Node.js.