Getting Started
Summary: Everything you need to install the SignalWire Agents SDK, create your first voice AI agent, and connect it to the SignalWire platform.
What You'll Learn
This chapter walks you through the complete setup process:
- Introduction - Understand what the SDK does and key concepts
- Installation - Install the SDK and verify it works
- Quick Start - Build your first agent in under 5 minutes
- Development Environment - Set up a professional development workflow
- Exposing Your Agent - Make your agent accessible to SignalWire using ngrok
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
- Python 3.8 or higher installed on your system
- pip (Python package manager)
- A terminal/command line interface
- A text editor or IDE (VS Code, PyCharm, etc.)
- (Optional) A SignalWire account for testing with real phone calls
Time to Complete
| Section | Time |
|---|---|
| Introduction | 5 min read |
| Installation | 5 min |
| Quick Start | 5 min |
| Dev Environment | 10 min |
| Exposing Agents | 10 min |
| Total | ~35 minutes |
By the End of This Chapter
You will have:
- A working voice AI agent
- Accessible via public URL
- Ready to connect to SignalWire phone numbers
SignalWire
What is the SignalWire Agents SDK?
The SignalWire Agents SDK lets you create voice AI agents - intelligent phone-based assistants that can:
- Answer incoming phone calls automatically
- Have natural conversations using AI (GPT-4, Claude, etc.)
- Execute custom functions (check databases, call APIs, etc.)
- Transfer calls, play audio, and manage complex call flows
- Scale from development to production seamlessly
How It Works
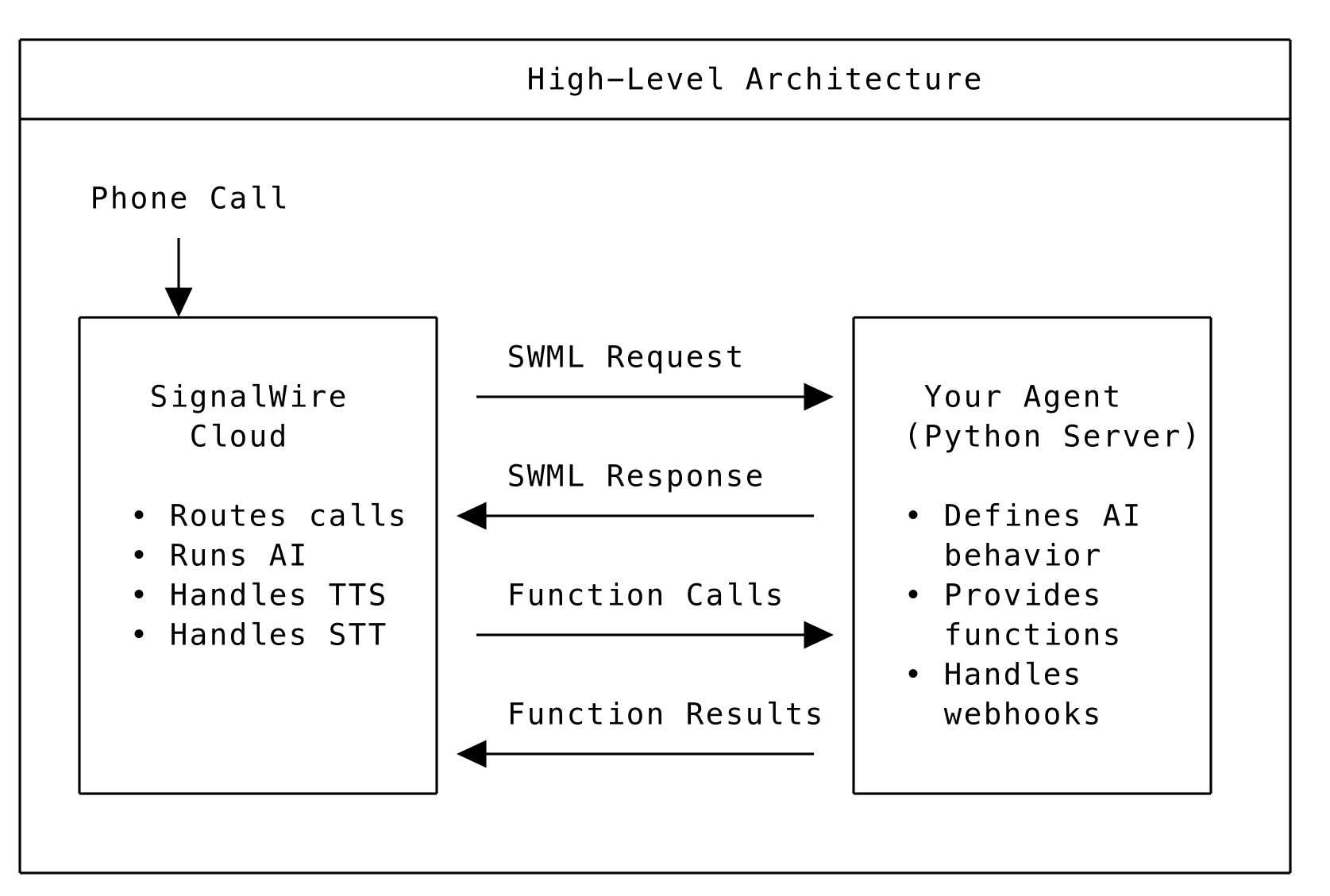
High-Level Architecture
The flow:
- A caller dials your SignalWire phone number
- SignalWire requests instructions from your agent (via HTTP)
- Your agent returns SWML (SignalWire Markup Language) - a JSON document describing how to handle the call
- SignalWire's AI talks to the caller based on your configuration
- When the AI needs to perform actions, it calls your SWAIG functions (webhooks)
- Your functions return results, and the AI continues the conversation
Key Concepts
Agent
An Agent is your voice AI application. It's a Python class that:
- Defines the AI's personality and behavior (via prompts)
- Provides functions the AI can call (SWAIG functions)
- Configures voice, language, and AI parameters
- Runs as a web server that responds to SignalWire requests
from signalwire_agents import AgentBase
class MyAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="my-agent")
# Configure your agent here
SWML (SignalWire Markup Language)
SWML is a JSON format that tells SignalWire how to handle calls. Your agent generates SWML automatically - you don't write it by hand.
{
"version": "1.0.0",
"sections": {
"main": [
{"answer": {}},
{"ai": {
"prompt": {"text": "You are a helpful assistant..."},
"SWAIG": {"functions": [...]}
}}
]
}
}
SWAIG Functions
SWAIG (SignalWire AI Gateway) functions are tools your AI can use during a conversation. When a caller asks something that requires action, the AI calls your function.
@agent.tool(description="Look up a customer by phone number")
def lookup_customer(args: dict, raw_data: dict = None) -> SwaigFunctionResult:
phone_number = args.get("phone_number", "")
customer = database.find(phone_number)
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"Customer: {customer.name}, Account: {customer.id}")
Skills
Skills are reusable plugins that add capabilities to your agent. The SDK includes built-in skills for common tasks:
datetime- Get current time and dateweb_search- Search the webweather_api- Get weather informationmath- Perform calculations
agent.add_skill("datetime")
agent.add_skill("web_search", google_api_key="...")
What You Can Build
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Customer Service | Answer FAQs, route calls, collect information |
| Appointment Scheduling | Book, reschedule, and cancel appointments |
| Surveys & Feedback | Conduct phone surveys, collect responses |
| IVR Systems | Interactive voice menus with AI intelligence |
| Receptionist | Screen calls, take messages, transfer to staff |
| Notifications | Outbound calls for alerts, reminders, confirmations |
The SDK includes prefab agents for common scenarios (InfoGatherer, FAQBot, Survey, Receptionist) that you can customize or use as starting points.
SDK Features
| Category | Features |
|---|---|
| Core | AgentBase class, SWAIG function decorators, Prompt building (POM), Voice & language config, Speech hints, Built-in skills |
| Advanced | Multi-step workflows (Contexts), Multi-agent servers, Call recording, Call transfer (SIP, PSTN), State management, Vector search integration |
| Deployment | Local dev server, Production (uvicorn), AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, Azure Functions, CGI mode, Docker/Kubernetes |
| Developer Tools | swaig-test CLI, SWML debugging, Function testing, Serverless simulation |
| Prefab Agents | InfoGathererAgent, FAQBotAgent, SurveyAgent, ReceptionistAgent, ConciergeAgent |
| DataMap | Direct API calls from SignalWire, No webhook server needed, Variable expansion, Response mapping |
Minimal Example
Here's the simplest possible agent:
from signalwire_agents import AgentBase
class HelloAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="hello")
self.prompt_add_section("Role", "You are a friendly assistant.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
agent = HelloAgent()
agent.run()
This agent:
- Starts a web server on port 3000
- Returns SWML that configures an AI assistant
- Uses the default voice and language settings
- Has no custom functions (just conversation)
Next Steps
Now that you understand what the SDK does, let's install it and build something real.

