Swml
SWML (SignalWire Markup Language)
Summary: SWML is the JSON format that tells SignalWire how to handle calls. Your agent generates SWML automatically - you configure the agent, and it produces the right SWML.
What is SWML?
SWML (SignalWire Markup Language) is a document that instructs SignalWire how to handle a phone call. SWML can be written in JSON or YAML format - this guide uses JSON throughout. When a call comes in, SignalWire requests SWML from your agent, then executes the instructions.
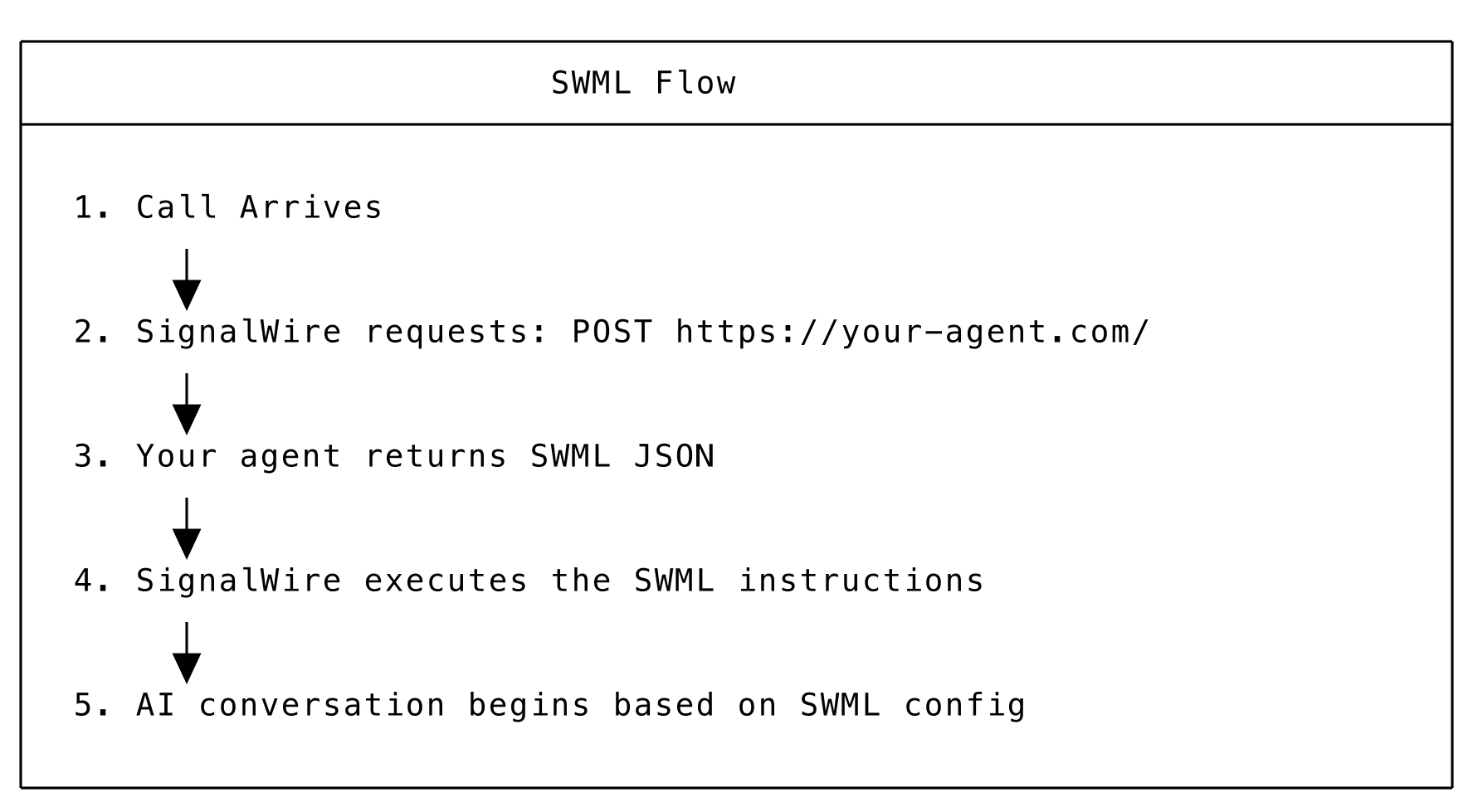
SWML Flow
SWML Document Structure
Every SWML document has this structure:
{
"version": "1.0.0",
"sections": {
"main": [
{ "verb1": { ...config } },
{ "verb2": { ...config } },
{ "verb3": { ...config } }
]
}
}
Key parts:
version: Always"1.0.0"sections: Contains named sections (usually justmain)- Each section is an array of verbs (instructions)
Common Verbs
| Verb | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
answer | Answer the incoming call | {"answer": {}} |
ai | Start AI conversation | {"ai": {...config}} |
connect | Transfer to another number | {"connect": {"to": "+1..."}} |
play | Play audio file | {"play": {"url": "..."}} |
record_call | Record the call | {"record_call": {"format": "mp4"}} |
hangup | End the call | {"hangup": {}} |
A Complete SWML Example
Here's what your agent generates:
{
"version": "1.0.0",
"sections": {
"main": [
{
"answer": {}
},
{
"ai": {
"prompt": {
"text": "# Role\nYou are a helpful customer service agent.\n\n# Guidelines\n- Be professional\n- Be concise"
},
"post_prompt": "Summarize what was discussed",
"post_prompt_url": "https://your-agent.com/post_prompt",
"SWAIG": {
"defaults": {
"web_hook_url": "https://your-agent.com/swaig"
},
"functions": [
{
"function": "get_balance",
"description": "Get the customer's account balance",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"account_id": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The account ID"
}
},
"required": ["account_id"]
}
}
]
},
"hints": ["account", "balance", "payment"],
"languages": [
{
"name": "English",
"code": "en-US",
"voice": "rime.spore"
}
],
"params": {
"end_of_speech_timeout": 500,
"attention_timeout": 15000
}
}
}
]
}
}
The ai Verb in Detail
The ai verb is the heart of voice AI agents. Here's what each part does:
{
"ai": {
"prompt": {}, // What the AI should do (system prompt)
"post_prompt": "...", // Instructions for summarizing the call
"post_prompt_url": "...",// Where to send the summary
"SWAIG": {}, // Functions the AI can call
"hints": [], // Words to help speech recognition
"languages": [], // Voice and language settings
"params": {}, // AI behavior parameters
"global_data": {} // Data available throughout the call
}
}
prompt
The AI's system prompt - its personality and instructions:
{
"prompt": {
"text": "You are a helpful assistant..."
}
}
Or using POM (Prompt Object Model):
{
"prompt": {
"pom": [
{
"section": "Role",
"body": "You are a customer service agent"
},
{
"section": "Rules",
"bullets": ["Be concise", "Be helpful"]
}
]
}
}
SWAIG
Defines functions the AI can call:
{
"SWAIG": {
"defaults": {
"web_hook_url": "https://your-agent.com/swaig"
},
"functions": [
{
"function": "check_order",
"description": "Check order status",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"order_id": {"type": "string"}
}
}
}
]
}
}
hints
Words that help speech recognition accuracy:
{
"hints": ["SignalWire", "SWML", "account number", "order ID"]
}
languages
Voice and language configuration:
{
"languages": [
{
"name": "English",
"code": "en-US",
"voice": "rime.spore"
}
]
}
params
AI behavior settings:
{
"params": {
"end_of_speech_timeout": 500,
"attention_timeout": 15000,
"barge_match_string": "stop|cancel|quit"
}
}
How Your Agent Generates SWML
You don't write SWML by hand. Your agent configuration becomes SWML:
from signalwire_agents import AgentBase
class MyAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="my-agent")
# This becomes languages in SWML
self.add_language("English", "en-US", "rime.spore")
# This becomes prompt in SWML
self.prompt_add_section("Role", "You are helpful.")
# This becomes hints in SWML
self.add_hints(["help", "support"])
# This becomes params in SWML
self.set_params({"end_of_speech_timeout": 500})
# This becomes SWAIG.functions in SWML
self.define_tool(
name="get_help",
description="Get help information",
parameters={},
handler=self.get_help
)
When SignalWire requests SWML, the agent's _render_swml() method:
- Collects all configuration (prompts, languages, hints, params)
- Builds the SWAIG functions array with webhook URLs
- Assembles the complete SWML document
- Returns JSON to SignalWire
SWML Rendering Pipeline
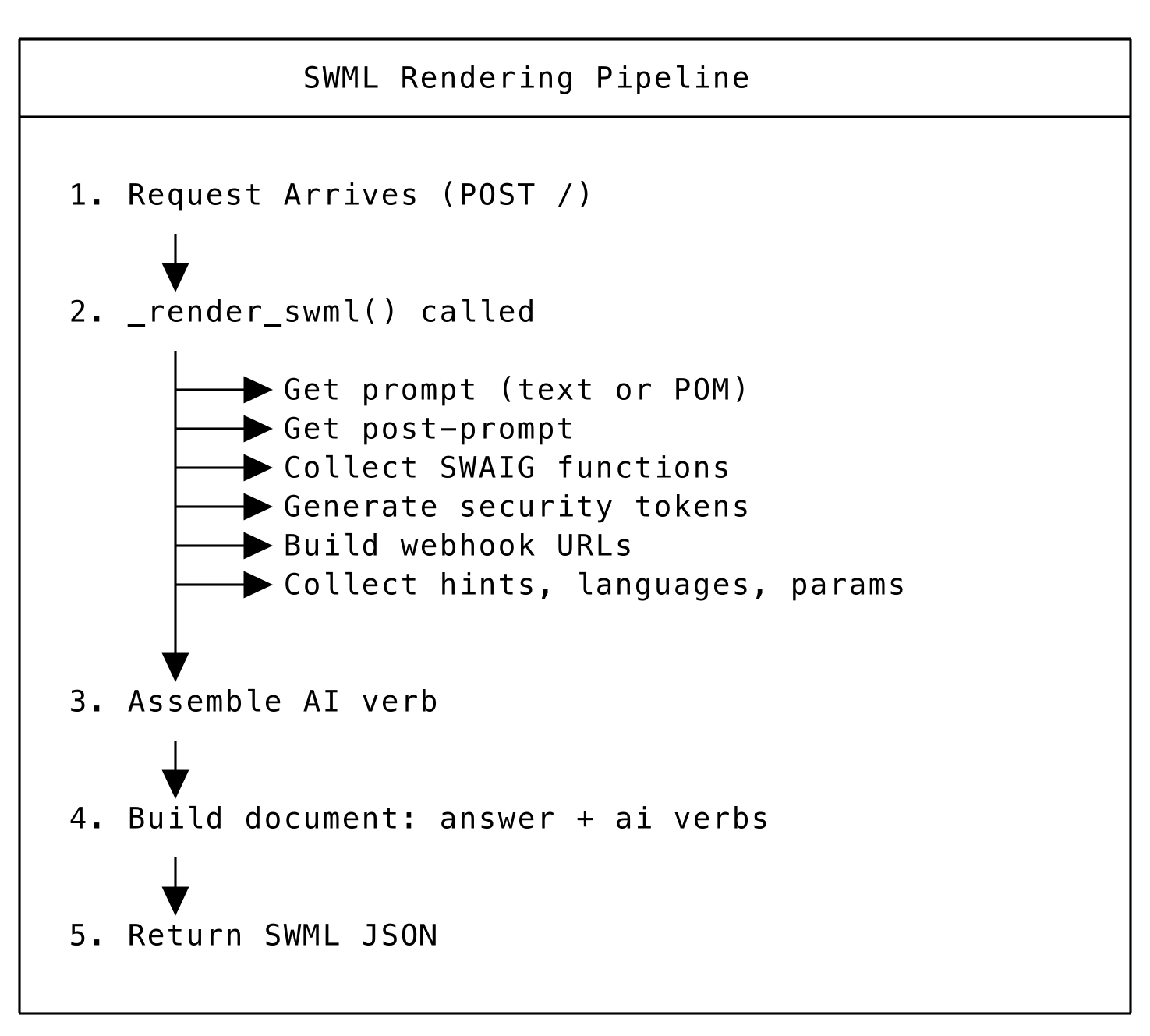
SWML Rendering Pipeline
Viewing Your SWML
You can see the SWML your agent generates:
## Using curl
curl http://localhost:3000/
## Using swaig-test CLI
swaig-test my_agent.py --dump-swml
## Pretty-printed
swaig-test my_agent.py --dump-swml --raw | jq '.'
SWML Schema Validation
The SDK validates SWML against the official schema:
- Located at
signalwire_agents/core/schema.json - Catches invalid configurations before sending to SignalWire
- Provides helpful error messages
Common SWML Patterns
Auto-Answer with AI
{
"version": "1.0.0",
"sections": {
"main": [
{"answer": {}},
{"ai": {...}}
]
}
}
Record the Call
{
"version": "1.0.0",
"sections": {
"main": [
{"answer": {}},
{"record_call": {"format": "mp4", "stereo": true}},
{"ai": {...}}
]
}
}
Transfer After AI
When a SWAIG function returns a transfer action, the SWML for transfer is embedded in the response:
{
"response": "Transferring you now",
"action": [
{"transfer": true},
{
"swml": {
"version": "1.0.0",
"sections": {
"main": [
{"connect": {"to": "+15551234567", "from": "+15559876543"}}
]
}
}
}
]
}
Next Steps
Now that you understand SWML structure, let's look at SWAIG - how AI calls your functions.