Hints
Hints
Summary: Speech hints improve recognition accuracy for domain-specific vocabulary, brand names, technical terms, and other words the STT engine might misinterpret.
Why Use Hints?
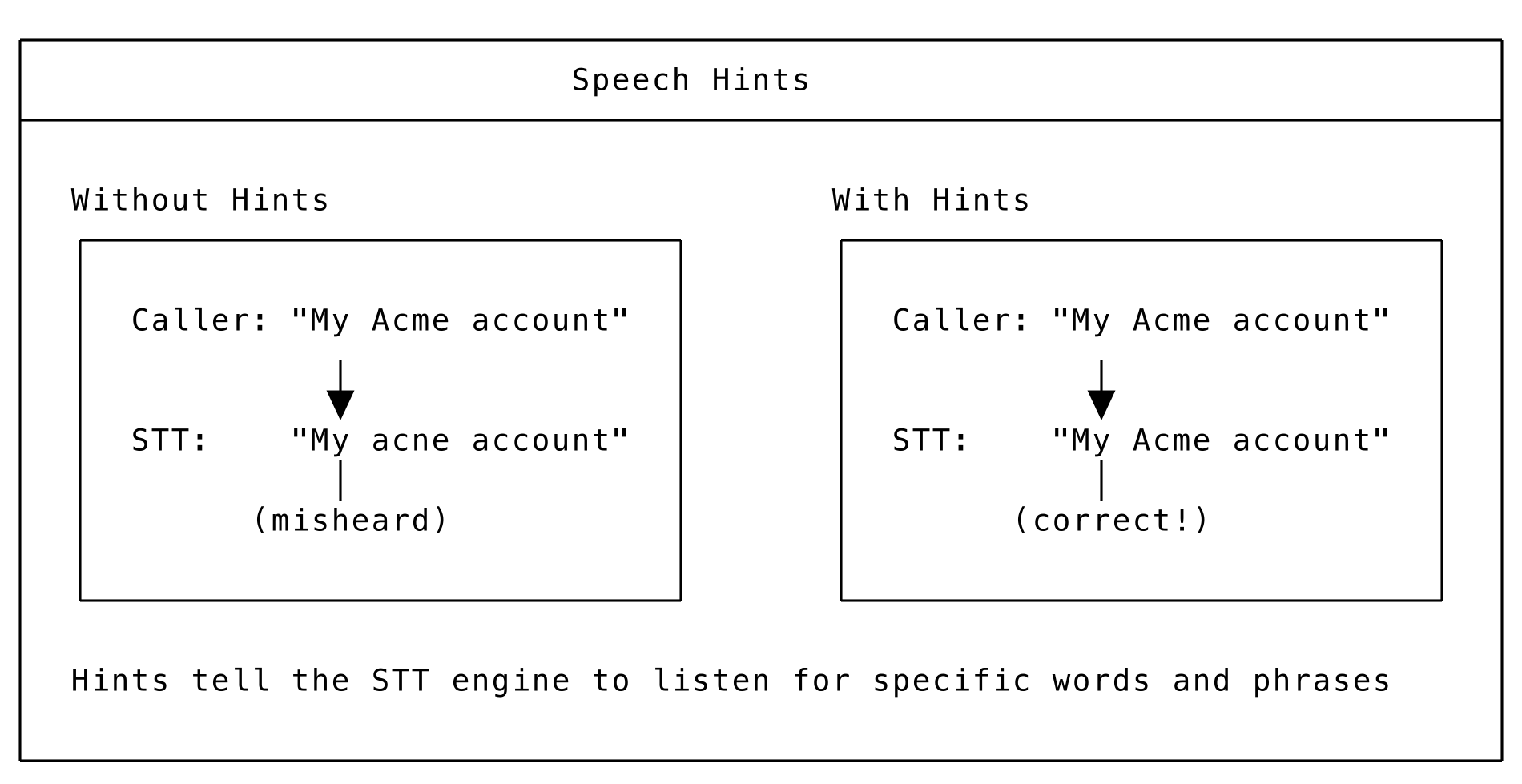
Speech Hints
Adding Simple Hints
Single Hint
from signalwire_agents import AgentBase
class MyAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="my-agent")
self.add_language("English", "en-US", "rime.spore")
# Add single hint
self.add_hint("Acme")
self.add_hint("SignalWire")
Multiple Hints
## Add list of hints
self.add_hints([
"Acme",
"SignalWire",
"API",
"webhook",
"SWML"
])
What to Hint
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Brand Names | Acme Corp, SignalWire, company name, product names |
| Technical Terms | API, webhook, OAuth, SDK, JSON |
| Industry Jargon | KYC, AML, SLA, EOD, PTO |
| Names | Employee names, customer names, location names |
| Numbers/Codes | Account numbers, ZIP codes, reference IDs |
| Actions | Transfer, escalate, reschedule |
Hint Examples by Use Case
Customer Service
self.add_hints([
# Brand and products
"Acme", "Acme Pro", "Acme Enterprise",
# Common actions
"account", "billing", "refund", "exchange", "return",
"cancel", "upgrade", "downgrade",
# Support terms
"representative", "supervisor", "escalate", "ticket",
"case number", "reference number"
])
Technical Support
self.add_hints([
# Product names
"Windows", "macOS", "Linux", "Chrome", "Firefox",
# Technical terms
"reboot", "restart", "reinstall", "cache", "cookies",
"browser", "firewall", "antivirus", "driver",
# Error terms
"error code", "blue screen", "crash", "freeze",
"not responding", "won't start"
])
Healthcare
self.add_hints([
# Appointment terms
"appointment", "reschedule", "cancel", "follow-up",
# Medical terms
"prescription", "refill", "pharmacy", "dosage",
"medication", "symptoms", "diagnosis",
# Department names
"cardiology", "dermatology", "pediatrics", "radiology",
# Common medications (if applicable)
"Tylenol", "Advil", "Lipitor", "Metformin"
])
Financial Services
self.add_hints([
# Account terms
"checking", "savings", "IRA", "401k", "Roth",
# Transaction terms
"transfer", "deposit", "withdrawal", "wire",
"ACH", "routing number", "account number",
# Services
"mortgage", "auto loan", "credit card", "overdraft",
# Verification
"social security", "date of birth", "mother's maiden name"
])
Pattern Hints (Advanced)
Pattern hints use regular expressions to match and normalize spoken input. They're useful for:
- Normalizing common mishearings of brand names
- Capturing structured data (account numbers, order IDs)
- Handling variations in how people say things
Pattern Hint Syntax
self.add_pattern_hint(
hint="what STT should listen for",
pattern=r"regex pattern to match",
replace="normalized output",
ignore_case=True # optional, default False
)
Common Pattern Examples
Brand name normalization:
# Catch common mishearings of "Acme"
self.add_pattern_hint(
hint="Acme",
pattern=r"(acme|ackme|ac me|acmee)",
replace="Acme",
ignore_case=True
)
# SignalWire variations
self.add_pattern_hint(
hint="SignalWire",
pattern=r"(signal wire|signalwire|signal-wire)",
replace="SignalWire",
ignore_case=True
)
Account/Order numbers:
# 8-digit account numbers
self.add_pattern_hint(
hint="account number",
pattern=r"\d{8}",
replace="${0}" # Keep the matched digits
)
# Order IDs like "ORD-12345"
self.add_pattern_hint(
hint="order ID",
pattern=r"ORD[-\s]?\d{5,8}",
replace="${0}",
ignore_case=True
)
Phone numbers:
# Various phone number formats
self.add_pattern_hint(
hint="phone number",
pattern=r"\d{3}[-.\s]?\d{3}[-.\s]?\d{4}",
replace="${0}"
)
Email addresses:
self.add_pattern_hint(
hint="email",
pattern=r"\S+@\S+\.\S+",
replace="${0}"
)
Dates:
# Dates like "January 15th" or "Jan 15"
self.add_pattern_hint(
hint="date",
pattern=r"(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)[a-z]*\s+\d{1,2}(st|nd|rd|th)?",
replace="${0}",
ignore_case=True
)
Pattern Hint Tips
Test patterns first:
Before adding pattern hints, test your regex at a site like regex101.com. STT output may vary from what you expect.
Start simple:
Begin with basic patterns and refine based on actual transcription errors you observe.
Use capture groups carefully:
${0}= entire match${1}= first capture group${2}= second capture group, etc.
Debug with logging:
Enable debug logging to see what STT produces, then craft patterns to match.
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
Order matters:
If multiple patterns could match, they're evaluated in registration order. Put more specific patterns first.
Organizing Hints
For large hint lists, organize by category:
class OrganizedHintsAgent(AgentBase):
# Hint categories
BRAND_HINTS = ["Acme", "Acme Pro", "Acme Enterprise"]
ACTION_HINTS = ["account", "billing", "refund", "cancel"]
SUPPORT_HINTS = ["representative", "supervisor", "escalate"]
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="organized-hints")
self.add_language("English", "en-US", "rime.spore")
# Add all hint categories
self.add_hints(self.BRAND_HINTS)
self.add_hints(self.ACTION_HINTS)
self.add_hints(self.SUPPORT_HINTS)
Dynamic Hints
Add hints based on context:
class DynamicHintsAgent(AgentBase):
DEPARTMENT_HINTS = {
"sales": ["pricing", "quote", "demo", "trial", "discount"],
"support": ["ticket", "bug", "error", "fix", "issue"],
"billing": ["invoice", "payment", "refund", "charge"]
}
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="dynamic-hints")
self.add_language("English", "en-US", "rime.spore")
# Common hints for all departments
self.add_hints(["Acme", "account", "help"])
def on_swml_request(self, request_data=None, callback_path=None, request=None):
call_data = (request_data or {}).get("call", {})
called_num = call_data.get("to", "")
# Add department-specific hints
if "555-1000" in called_num:
self.add_hints(self.DEPARTMENT_HINTS["sales"])
elif "555-2000" in called_num:
self.add_hints(self.DEPARTMENT_HINTS["support"])
else:
self.add_hints(self.DEPARTMENT_HINTS["billing"])
Hint Best Practices
DO:
- Hint brand names and product names
- Hint technical terms specific to your domain
- Hint common employee/customer names
- Hint acronyms and abbreviations
- Test with actual callers to find missed words
DON'T:
- Hint common English words (already recognized well)
- Add hundreds of hints (quality over quantity)
- Hint full sentences (single words/short phrases work best)
- Forget to update hints when products/terms change
Testing Hints
Use swaig-test to verify hints are included:
## View SWML including hints
swaig-test my_agent.py --dump-swml | grep -A 20 "hints"
Check the generated SWML for the hints array:
{
"version": "1.0.0",
"sections": {
"main": [{
"ai": {
"hints": [
"Acme",
"SignalWire",
"account",
"billing"
]
}
}]
}
}
Complete Example
#!/usr/bin/env python3
## hinted_agent.py - Agent with speech recognition hints
from signalwire_agents import AgentBase, SwaigFunctionResult
class HintedAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="hinted-agent")
self.add_language("English", "en-US", "rime.spore")
# Brand hints
self.add_hints([
"Acme", "Acme Pro", "Acme Enterprise",
"AcmePay", "AcmeCloud"
])
# Product SKUs
self.add_hints([
"SKU", "A100", "A200", "A300",
"PRO100", "ENT500"
])
# Common actions
self.add_hints([
"account", "billing", "invoice", "refund",
"cancel", "upgrade", "downgrade",
"representative", "supervisor"
])
# Technical terms
self.add_hints([
"API", "webhook", "integration",
"OAuth", "SSO", "MFA"
])
self.prompt_add_section(
"Role",
"You are a customer service agent for Acme Corporation."
)
self.define_tool(
name="lookup_product",
description="Look up product by SKU",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"sku": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Product SKU like A100 or PRO100"
}
},
"required": ["sku"]
},
handler=self.lookup_product
)
def lookup_product(self, args, raw_data):
sku = args.get("sku", "").upper()
products = {
"A100": "Acme Basic - $99/month",
"A200": "Acme Standard - $199/month",
"A300": "Acme Premium - $299/month",
"PRO100": "Acme Pro - $499/month",
"ENT500": "Acme Enterprise - Custom pricing"
}
if sku in products:
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"{sku}: {products[sku]}")
return SwaigFunctionResult(f"SKU {sku} not found.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
agent = HintedAgent()
agent.run()
Next Steps
You now know how to build and configure agents. Next, learn about SWAIG functions to add custom capabilities.