Advanced Features
Summary: This chapter covers advanced SDK features including multi-step workflows with contexts, state management, call recording, call transfers, multi-agent servers, and knowledge search integration.
The features in this chapter build on the fundamentals covered earlier. While basic agents handle free-form conversations well, many real-world applications require more structure: guided workflows that ensure certain information is collected, the ability to transfer between different "departments" or personas, recording for compliance, and integration with knowledge bases.
These advanced features transform simple voice agents into sophisticated conversational applications capable of handling complex business processes.
What You'll Learn
This chapter covers advanced capabilities:
- Contexts & Workflows - Multi-step conversation flows with branching logic
- State Management - Session data, global state, and metadata handling
- Call Recording - Record calls with various formats and options
- Call Transfer - Transfer calls to other destinations
- Multi-Agent Servers - Run multiple agents on a single server
- Search & Knowledge - Vector search for RAG-style knowledge integration
Feature Overview
Contexts & Workflows
- Multi-step conversations
- Branching logic
- Context switching
- Step validation
State Management
- global_data dictionary
- metadata per call
- Tool-specific tokens
- Post-prompt data injection
Call Recording
- Stereo/mono recording
- Multiple formats (mp3, wav, mp4 for video)
- Pause/resume control
- Transcription support
Call Transfer
- Blind transfers
- Announced transfers
- SIP destinations
- PSTN destinations
Multi-Agent Servers
- Multiple agents per server
- Path-based routing
- SIP username routing
- Shared configuration
Search & Knowledge
- Vector similarity search
- SQLite/pgvector backends
- Document processing
- RAG integration
When to Use These Features
| Feature | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Contexts | Multi-step forms, wizards, guided flows |
| State Management | Persisting data across function calls |
| Call Recording | Compliance, training, quality assurance |
| Call Transfer | Escalation, routing to humans |
| Multi-Agent | Different agents for different purposes |
| Search | Knowledge bases, FAQ lookup, documentation |
Prerequisites
Before diving into advanced features:
- Understand basic agent creation (Chapter 3)
- Know how SWAIG functions work (Chapter 4)
- Be comfortable with skills (Chapter 5)
Chapter Contents
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Contexts & Workflows | Build multi-step conversation flows |
| State Management | Manage session and call state |
| Call Recording | Record calls with various options |
| Call Transfer | Transfer calls to destinations |
| Multi-Agent | Run multiple agents on one server |
| Search & Knowledge | Vector search integration |
When to Use Contexts
Contexts are the SDK's answer to a common challenge: how do you ensure a conversation follows a specific path? Regular prompts work well for open-ended conversations, but many business processes require structure—collecting specific information in a specific order, or routing callers through a defined workflow.
Think of contexts as conversation "states" or "modes." Each context can have its own persona, available functions, and series of steps. The AI automatically manages transitions between contexts and steps based on criteria you define.
| Regular Prompts | Contexts |
|---|---|
| Free-form conversations | Structured workflows |
| Simple Q&A agents | Multi-step data collection |
| Single-purpose tasks | Wizard-style flows |
| No defined sequence | Branching conversations |
| Multiple personas |
Use contexts when you need:
- Guaranteed step completion
- Controlled navigation
- Step-specific function access
- Context-dependent personas
- Department transfers
- Isolated conversation segments
Common context patterns:
- Data collection wizard: Gather customer information step-by-step (name → address → payment)
- Triage flow: Qualify callers before routing to appropriate department
- Multi-department support: Sales, Support, and Billing each with their own persona
- Appointment scheduling: Check availability → select time → confirm details
- Order processing: Select items → confirm order → process payment
Context Architecture
Understanding how contexts, steps, and navigation work together is essential for building effective workflows.
Key concepts:
- ContextBuilder: The top-level container that holds all your contexts
- Context: A distinct conversation mode (like "sales" or "support"), with its own persona and settings
- Step: A specific point within a context where certain tasks must be completed
The AI automatically tracks which context and step the conversation is in. When step criteria are met, it advances to the next allowed step. When context navigation is permitted and appropriate, it switches contexts entirely.
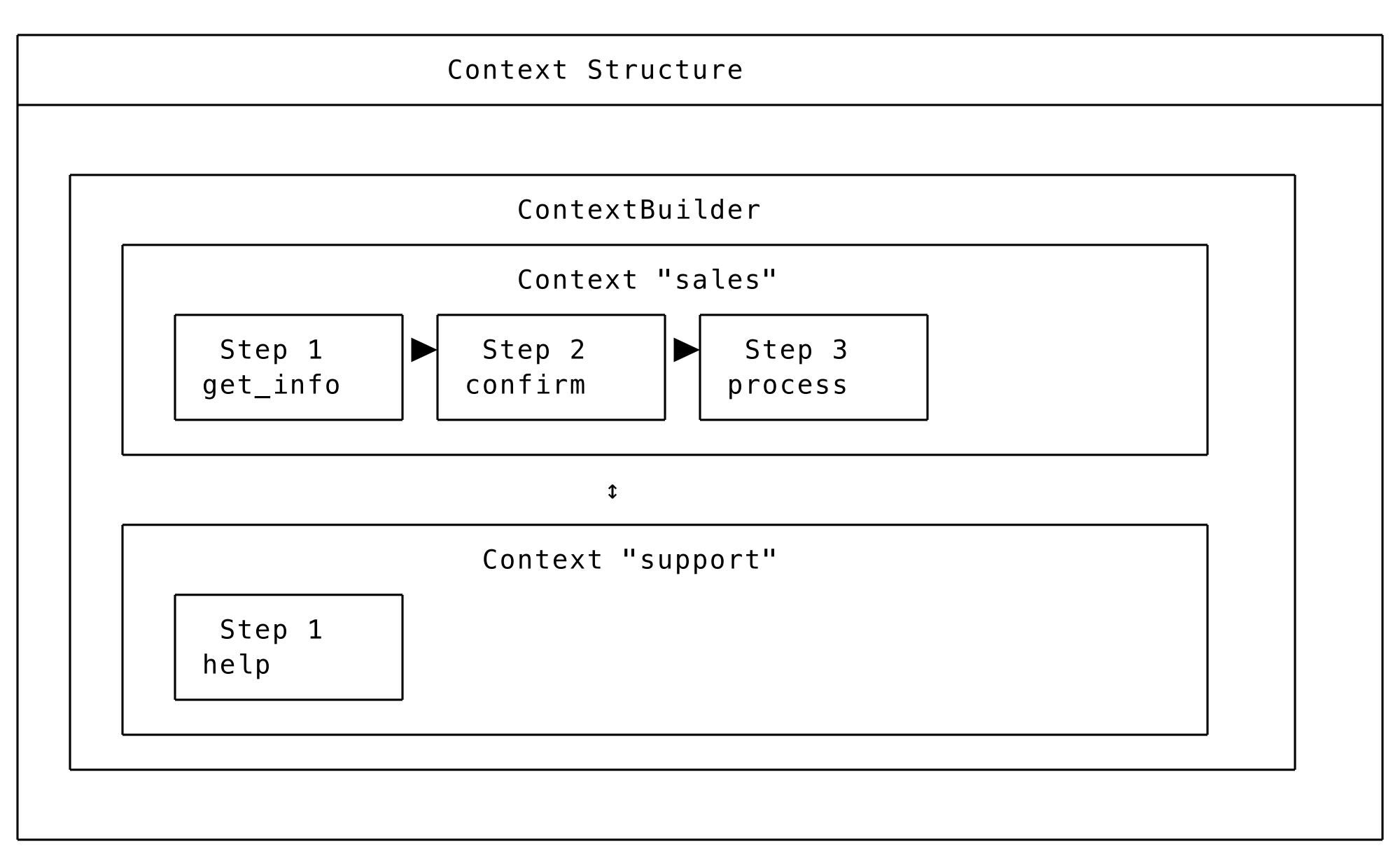
Context Structure
How state flows through contexts:
- Caller starts in the first step of the default (or specified) context
- AI follows the step's instructions until
step_criteriais satisfied - AI chooses from
valid_stepsto advance within the context - If
valid_contextsallows, AI can switch to a different context entirely - When switching contexts,
isolated,consolidate, orfull_resetsettings control what conversation history carries over
Basic Context Example
from signalwire_agents import AgentBase
class OrderAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="order-agent")
self.add_language("English", "en-US", "rime.spore")
# Base prompt (required even with contexts)
self.prompt_add_section(
"Role",
"You help customers place orders."
)
# Define contexts after setting base prompt
contexts = self.define_contexts()
# Add a context with steps
order = contexts.add_context("default")
order.add_step("get_item") \
.set_text("Ask what item they want to order.") \
.set_step_criteria("Customer has specified an item") \
.set_valid_steps(["get_quantity"])
order.add_step("get_quantity") \
.set_text("Ask how many they want.") \
.set_step_criteria("Customer has specified a quantity") \
.set_valid_steps(["confirm"])
order.add_step("confirm") \
.set_text("Confirm the order details and thank them.") \
.set_step_criteria("Order has been confirmed")
if __name__ == "__main__":
agent = OrderAgent()
agent.run()
Step Configuration
set_text()
Simple text prompt for the step:
step.set_text("What item would you like to order?")
add_section() / add_bullets()
POM-style structured prompts:
step.add_section("Task", "Collect customer information") \
.add_bullets("Required Information", [
"Full name",
"Phone number",
"Email address"
])
set_step_criteria()
Define when the step is complete:
step.set_step_criteria("Customer has provided their full name and phone number")
set_valid_steps()
Control step navigation:
# Can go to specific steps
step.set_valid_steps(["confirm", "cancel"])
# Use "next" for sequential flow
step.set_valid_steps(["next"])
set_functions()
Restrict available functions per step:
# Disable all functions
step.set_functions("none")
# Allow specific functions only
step.set_functions(["check_inventory", "get_price"])
set_valid_contexts()
Allow navigation to other contexts:
step.set_valid_contexts(["support", "manager"])
Understanding Step Criteria
Step criteria tell the AI when a step is "complete" and it's time to move on. Writing good criteria is crucial—too vague and the AI may advance prematurely; too strict and the conversation may get stuck.
Good criteria are:
- Specific and measurable
- Phrased as completion conditions
- Focused on what information has been collected
Examples of well-written criteria:
# Good: Specific, measurable
.set_step_criteria("Customer has provided their full name and email address")
# Good: Clear completion condition
.set_step_criteria("Customer has selected a product and confirmed the quantity")
# Good: Explicit confirmation
.set_step_criteria("Customer has verbally confirmed the order total")
Problematic criteria to avoid:
# Bad: Too vague
.set_step_criteria("Customer is ready")
# Bad: Subjective
.set_step_criteria("Customer seems satisfied")
# Bad: No clear completion point
.set_step_criteria("Help the customer")
Context Configuration
set_isolated()
Truncate conversation history when entering:
context.set_isolated(True)
set_system_prompt()
New system prompt when entering context:
context.set_system_prompt("You are now a technical support specialist.")
set_user_prompt()
Inject a user message when entering:
context.set_user_prompt("I need help with a technical issue.")
set_consolidate()
Summarize previous conversation when switching:
context.set_consolidate(True)
set_full_reset()
Completely reset conversation state:
context.set_full_reset(True)
add_enter_filler() / add_exit_filler()
Add transition phrases:
context.add_enter_filler("en-US", [
"Let me connect you with our support team...",
"Transferring you to a specialist..."
])
context.add_exit_filler("en-US", [
"Returning you to the main menu...",
"Back to the sales department..."
])
Multi-Context Example
from signalwire_agents import AgentBase
class MultiDepartmentAgent(AgentBase):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(name="multi-dept-agent")
self.add_language("English-Sales", "en-US", "rime.spore")
self.add_language("English-Support", "en-US", "rime.cove")
self.add_language("English-Manager", "en-US", "rime.marsh")
self.prompt_add_section(
"Instructions",
"Guide customers through sales or transfer to appropriate departments."
)
contexts = self.define_contexts()
# Sales context
sales = contexts.add_context("sales") \
.set_isolated(True) \
.add_section("Role", "You are Alex, a sales representative.")
sales.add_step("qualify") \
.add_section("Task", "Determine customer needs") \
.set_step_criteria("Customer needs are understood") \
.set_valid_steps(["recommend"]) \
.set_valid_contexts(["support", "manager"])
sales.add_step("recommend") \
.add_section("Task", "Make product recommendations") \
.set_step_criteria("Recommendation provided") \
.set_valid_contexts(["support", "manager"])
# Support context
support = contexts.add_context("support") \
.set_isolated(True) \
.add_section("Role", "You are Sam, technical support.") \
.add_enter_filler("en-US", [
"Connecting you with technical support...",
"Let me transfer you to our tech team..."
])
support.add_step("assist") \
.add_section("Task", "Help with technical questions") \
.set_step_criteria("Technical issue resolved") \
.set_valid_contexts(["sales", "manager"])
# Manager context
manager = contexts.add_context("manager") \
.set_isolated(True) \
.add_section("Role", "You are Morgan, the store manager.") \
.add_enter_filler("en-US", [
"Let me get the manager for you...",
"One moment, connecting you with management..."
])
manager.add_step("escalate") \
.add_section("Task", "Handle escalated issues") \
.set_step_criteria("Issue resolved by manager") \
.set_valid_contexts(["sales", "support"])
if __name__ == "__main__":
agent = MultiDepartmentAgent()
agent.run()
Navigation Flow
Within Context (Steps)
set_valid_steps(["next"])- Go to next sequential stepset_valid_steps(["step_name"])- Go to specific stepset_valid_steps(["a", "b"])- Multiple options
Between Contexts
set_valid_contexts(["other_context"])- Allow context switch- AI calls
change_context("context_name")automatically - Enter/exit fillers provide smooth transitions
Context Entry Behavior
isolated=True- Clear conversation historyconsolidate=True- Summarize previous conversationfull_reset=True- Complete prompt replacement
Validation Rules
The ContextBuilder validates your configuration:
- Single context must be named "default"
- Every context must have at least one step
valid_stepsmust reference existing steps (or "next")valid_contextsmust reference existing contexts- Cannot mix
set_text()withadd_section()on same step - Cannot mix
set_prompt()withadd_section()on same context
Step and Context Methods Summary
| Method | Level | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
set_text() | Step | Simple text prompt |
add_section() | Both | POM-style section |
add_bullets() | Both | Bulleted list section |
set_step_criteria() | Step | Completion criteria |
set_functions() | Step | Restrict available functions |
set_valid_steps() | Step | Allowed step navigation |
set_valid_contexts() | Both | Allowed context navigation |
set_isolated() | Context | Clear history on entry |
set_consolidate() | Context | Summarize on entry |
set_full_reset() | Context | Complete reset on entry |
set_system_prompt() | Context | New system prompt |
set_user_prompt() | Context | Inject user message |
add_enter_filler() | Context | Entry transition phrases |
add_exit_filler() | Context | Exit transition phrases |
Context Switching Behavior
When the AI switches between contexts, several things can happen depending on your configuration. Understanding these options helps you create smooth transitions.
Isolated Contexts
When isolated=True, the conversation history is cleared when entering the context. This is useful when:
- You want a clean slate for a new department
- Previous context shouldn't influence the new persona
- You're implementing strict separation between workflow segments
support = contexts.add_context("support") \
.set_isolated(True) # Fresh start when entering support
The caller won't notice—the AI simply starts fresh with no memory of the previous context.
Consolidated Contexts
When consolidate=True, the AI summarizes the previous conversation before switching. This preserves important information without carrying over the full history:
billing = contexts.add_context("billing") \
.set_consolidate(True) # Summarize previous conversation
The summary includes key facts and decisions, giving the new context awareness of what happened without the full transcript.
Full Reset Contexts
full_reset=True goes further than isolation—it completely replaces the system prompt and clears all state:
escalation = contexts.add_context("escalation") \
.set_full_reset(True) # Complete prompt replacement
Use this when the new context needs to behave as if it were a completely different agent.
Combining with Enter/Exit Fillers
Fillers provide audio feedback during context switches, making transitions feel natural:
support = contexts.add_context("support") \
.set_isolated(True) \
.add_enter_filler("en-US", [
"Let me transfer you to technical support.",
"One moment while I connect you with a specialist."
]) \
.add_exit_filler("en-US", [
"Returning you to the main menu.",
"Transferring you back."
])
The AI randomly selects from the filler options, providing variety in the transitions.
Debugging Context Flows
When contexts don't behave as expected, use these debugging strategies:
-
Check step criteria: If stuck on a step, the criteria may be too strict. Temporarily loosen them to verify the flow works.
-
Verify navigation paths: Ensure
valid_stepsandvalid_contextsform a complete graph. Every step should have somewhere to go (unless it's a terminal step). -
Test with swaig-test: The testing tool shows context configuration in the SWML output:
swaig-test your_agent.py --dump-swml | grep -A 50 "contexts"
-
Add logging in handlers: If you have SWAIG functions, log when they're called to trace the conversation flow.
-
Watch for validation errors: The ContextBuilder validates your configuration at runtime. Check logs for validation failures.
Best Practices
DO:
- Set clear step_criteria for each step
- Use isolated=True for persona changes
- Add enter_fillers for smooth transitions
- Define valid_contexts to enable department transfers
- Test navigation paths thoroughly
- Provide escape routes from every step (avoid dead ends)
- Use consolidate=True when context needs awareness of previous conversation
DON'T:
- Create circular navigation without exit paths
- Skip setting a base prompt before define_contexts()
- Mix set_text() with add_section() on the same step
- Forget to validate step/context references
- Use full_reset unless you truly need a complete persona change
- Make criteria too vague or too strict